 The Smart Card Middleware (MW) enables the computer applications to communicate with smart cards using standardized application programming interfaces (APIs).
The Smart Card Middleware (MW) enables the computer applications to communicate with smart cards using standardized application programming interfaces (APIs).
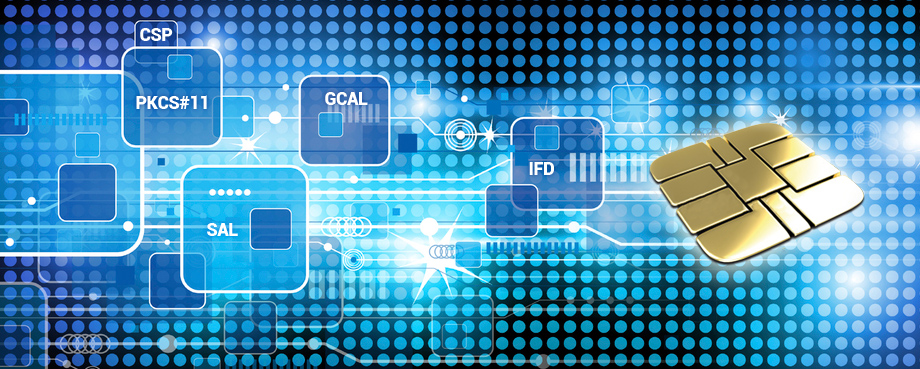
The MW architecture and its functionality are based on the corresponding actual standards and technical guidelines, in particular on
The low level implementation features of the smart card, including proprietary specific features and characteristics, are hidden to the client application through a high-level description provided to the terminal and processed by the middleware stack.
The middleware stack is defined by abstraction layers ensuring the interoperability. ISO/IEC 242727 MW abstraction layers:
Service Access Layer (SAL) is in charge of interpreting the requests addressed by the client-application to the card via a high-level API (the SAL-API), the SAL is specified in ISO/IEC 24727-3.
Generic Card Access Layer (GCAL) is in charge of translating the smart card commands (APDU) handled on by the SAL in terms of APDU understandable to the smart card, the GCAL is specified in ISO/IEC 24727-2.
The ISO/IEC 242727 architecture of the Smart Card MW enables a web-based application running on a service provider’s server to communicate with a remote smart card through a secured communication channel.
